
Plants need plenty of sun, air, water, and nutrients to grow. But how can you make sure your plants have enough nutrients? Measuring different aspects of soil can tell you exactly what you need and what you are missing, and help you to foster strong and healthy plants. This post will explore the importance of Why Measure Soil EC?
Testing the pH, moisture content, and temperature of your soil are a good start for healthy soil. Monitoring phosphates, nitrates, calcium, and potassium are all primary components to plant growth. Other minor nutrients are needed as well.
One way to help keep track of all these nutrients is by testing the electrical conductivity of your soil. Electrical conductivity can tell you if you need more nutrients, or if you have too much. This will save you time and money when managing your plants.
For controlled-environment-grown crops, substrate pH and electrical conductivity (EC) are two main factors that can easily be monitored to make sure your crop is on track for success. This monitoring principle has been used by the commercial floriculture industry for the past 40 years. Monitoring and managing the substrate pH and EC could help to avoid up to 80 percent of the plant nutrition problems that occur with controlled environment crops
Importance of Knowing Your Soil EC

Testing your soil is all about making sure the nutrients are balanced. Measuring the pH of soil gives you an idea of how available the nutrients are, while EC clues you into how much is actually there. Remember that EC is good at giving a measurement of the strength of the ions in the soil. This helps you to track the nutrients that are available to your plants.
There is a high correlation of better crop yield to the use of electrical conductivity soil maps. Like topography maps, there are maps that show the EC of various geographic areas. You can create an EC map of your own; test the EC of different areas and plot it on a map.
What is EC?
Electrical conductivity is the electrical charge that moves through a solution. The higher the salt concentration, the greater the electrical reading. This principle is applied to controlled environment production because the higher the concentration of fertilizer salts in the solution or in the substrate, the higher the EC reading will be. We can then monitor the EC level to ensure that fertility levels are where they need to be. Why Measure Soil EC?
Check-It’s Smart Growing Monitoring solution allows you to set alerts to warn when your actual EC drifts into unwanted territory. Recommended corrective actions (actionable data) will be provided so that take the necessary steps to get back to your sweet spot. Below are the standard corrective procedures used to modify the substrate EC for controlled environment plants grown in soilless substrates and adapted for cannabis.
1. Low Substrate EC Corrective Action (deficiency)
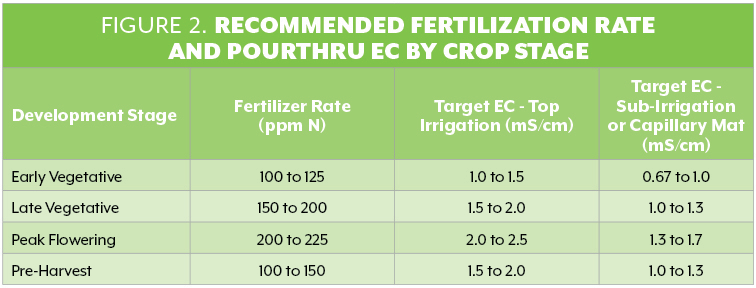
If the levels are lower than the recommended range (Fig. 2, below), this implies the plant’s nutrient demand is higher than what is being supplied. In this case, you must increase the fertilizer rate. One or two applications of a higher N rate in the 250-ppm to 400-ppm range will boost the EC.
2. High Substrate EC Corrective Action (nutrient build up)
EC levels that increase over time indicate the fertilizer is accumulating in the pot and the rate is higher than the demand by the plant. The first step in addressing this is dialing back the fertilizer rate to moderate the accumulation of fertilizer salts. (This also will help save money by not wasting fertilizer solution.)
The second option is to irrigate the plant substrate twice with clear water to leach out the fertilizer salts. This method is used to help avoid plant burn when EC levels are extremely high. It also flushes out your fertilizer investment. Monitoring the crop during production will help you avoid these elevated levels in the first place.
What Does EC Measure
The EC is a measurement of the total amount of fertilizer salts in the solution. It does not provide specific information about each individual element or that individual element’s concentration in solution. Why Measure Soil EC?
In controlled environment production, the primary nutrients we provide are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). Therefore, with most cases in both theory and practice, the EC reflects the relative concentration of those elements. You can apply this concept to cannabis to confirm the accuracy of the fertilizer concentration you apply in the solution and to monitor the crop’s nutritional status.
Know Your Water
You must also take into account the EC contribution of your water source as it contributes to the Soil EC. If your irrigation water has high concentrations of alkalinity (calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) or sodium (Na)) then when you test the EC of your fertilizer solution or substrate, your values will be artificially elevated, too. When monitoring the fertilizer solution you are supplying to the plants, knowing the EC contribution of your irrigation water is important. This requires that you periodically have your water quality tested by a commercial lab.
Figure 2, Illustrates the recommended Nitrogen rates and Target EC recommendations for different growth stages of Cannabis.
Our Smart Growing Solution is simple and intuitive and will allow you to find your “Sweet-Spot”. Contact us to get started.https://site.check-it.ca/reach-out/. We have experience working with growers and provide solutions that are reliable and proven, we have been around since 2008.
#smartgrow #IoT #agtech #microcultivator #SKtech #idealgrowing #perfectenvironment #cannabis #smartgreenhouse
#greenhouse
